
|
||
| Release 4.0 | ||
 |
Escapetime - Iteration Formulas
Iteration formulas are the most important formulas in
ChaosPro: They define the fractal formula used to calculate the fractal, for
example z^2+c or sin(z)+c. So this formula is responsible for the
complexity of the fractal, i.e. the detail level and its shape.
The following three images show the same area using exactly the same settings except the iteration formula.
 Newton |
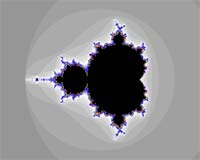 Classical |
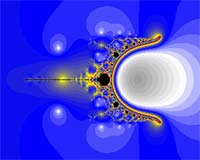 Magnet |
Such an iteration formula may contain the following functions:
- void init_once(void): Called only once, i.e. when the fractal calculation starts: In this routine you can initialize variables and allocate arrays.
- void init(void): This init routine gets executed for each pixel before the actual fractal loop starts. Its purpose is to do some initializations for the formula. Please remember that variables do not have an initial value. They are uninitialized and contain random values at the beginning. So initialize them in this function or in init_once...
- void loop(void): This function defines the main iteration formula. For the classical mandelbrot set it would contain
z=z^2+c. After the init function the main iteration loop starts: This function gets executed until the maximum number of iterations has been reached or the bailout function returns false. - bool bailout(void): After each loop this function is executed in order to determine whether the value of the iteration has "bailed out". If this
function returns
false, the iteration stops. If it returnstrue, the iteration loop continues until the maximum number of iterations has been reached. - void description(void): An iteration formula also may (must) contain a function named description.
The bailout function must return a boolean data type and must consist of a single expression of the form:
bool bailout(void)
{
return(boolean-expression);
}
So you cannot make complex if-then-else statements with for-loops in the bailout function. If you do want to program more complex bailout expressions you can place the complex code at the end of the loop function and set a bool variable. In the bailout section you then simply return that bool variable.
The main reason for this limiting single-expression-function is speed: ChaosPro can simply evaluate the expression knowing that it returns the final result as a bool type. Otherwise there could be many branches in the execution path where the iteration bails out.
Example
def_mand {
parameter complex criticalpoint;
parameter complex power;
parameter real bailout;
void init_once(void)
{
// nothing useful to do here...
}
void init(void)
{
z=criticalpoint;
}
void loop(void)
{
z=z^2 + pixel;
}
bool bailout(void)
{
return(|z| <= bailout);
}
void description(void)
{
this.title = "Mandelbrot";
this.helpfile = "dmj3\dmj3-pub-uf-ot.htm";
power.caption = "Power";
power.default = center+(2,3);
power.hint = "Choose the exponent of the iteration formula for the Julia set.\nHigher (int-) values just lead to some kind of rotation symmetry. So try fractional or even complex numbers.";
bailout.caption = "Bailout Value";
bailout.default = 4.0;
bailout.min = 1.0;
bailout.hint = "Defines the bailout radius: As soon as a pixel falls outside a circle with this radius, the iteration stops.";
}
}










